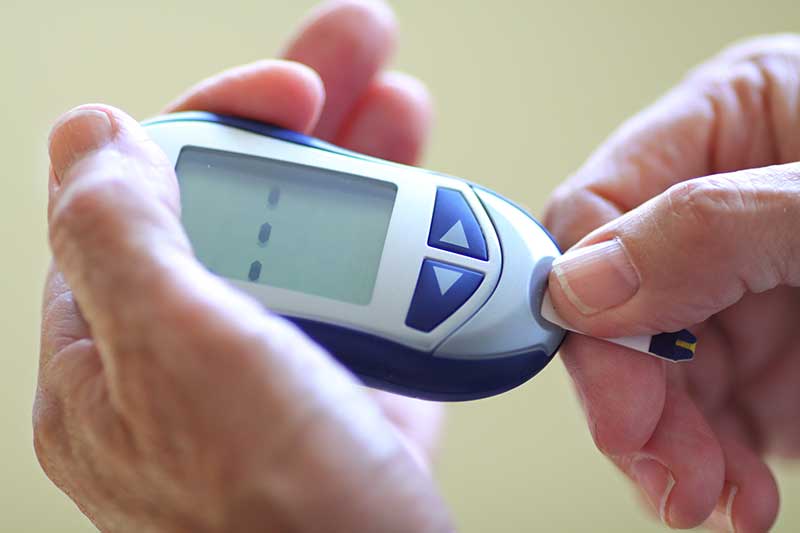
Aug 22, 2017
It is estimated that 86 million Americans (more than one out of three) has “pre-diabetes,” which develops before type-2 diabetes. Moreover, 90 percent of these individuals are unaware that they are pre-diabetic. Pre-diabetes is characterized by blood glucose levels...

Aug 15, 2017
One of the primary complaints of older hearing instruments revolved around the problem of “acoustic feedback,” which occurs when some of the amplified sound leaks from the ear canal back into the microphone and becomes re-amplified. This cycle of leakage and...
Aug 8, 2017
The term “cocktail party effect” refers to the human ability to focus on a single speaker while tuning out noisy background noise. Research indicates that the left side of our brains picks out the desired sounds from the background noise. This makes sense when you...

Aug 1, 2017
According to recent statistics released by the Hearing Industries Association (HIA), “open-fit” hearing instruments now account for more than half of all hearing instruments sold in the United States. This category, which includes “receiver-in-the-canal” (RIC) and...

Jul 25, 2017
Sometimes we may raise our voices only slightly to get the attention of a person with hearing loss, only to have that person respond, “You don’t have to yell. I’m not deaf!” This type of encounter provides anecdotal evidence of a phenomenon known as “recruitment,”...

Jul 18, 2017
An “acoustic neuroma,” the most common inner ear tumor, begins growing within the inner ear. “Vestibular schwannoma,” as the tumor is also known, forms when Schwann cells, which wrap themselves in layers around the auditory nerve, grow too rapidly. It is important to...







